A lot of people tend to dismiss eczema as a childhood ailment, but this simply is not the case; eczema can affect adults too. The truth is that having eczema as an adult can be debilitating. It can have a profound effect on not only your physical health but your mental health too. Eczema tends to present similarly regardless of the age of the sufferer, but there are a few differences, let’s explore.
Dealing With Eczema as an Adult

The Facts on Adult Eczema
Eczema, as mentioned above, affects adults. Most of the time, an individual will suffer from eczema from childhood, or they will have suffered as a child, and eczema will recur during their adult life. In some rare cases, adults can develop eczema for the first time in their life.
Eczema is one of the most common forms of skin condition in the UK. One-in-five children suffer and one-in-ten adults. There are several forms of eczema, and any one of them can affect adults, although there are a few different forms that are more common in adults than children. Eczema occurs because the barrier of the skin is faulty or weak; it simply cannot retain moisture or keep irritants out.
Adult Eczema Symptoms
The symptoms of eczema remain largely unchanged whether you are suffering as a child or an adult. The symptoms tend to include things like intense itchiness; the itch can be so severe that It keeps you up at night. In addition, suffering from eczema is often linked to asthma, hay fever, and allergies in general, so if you have any of these, it can make it more likely that you also have eczema.
You might also suffer from skin infections, rashes, and inflammation, and dry patches themselves can occur anywhere on the body, but they are often found in the crooks of the elbows, behind the knees, the neck, and around the eyes. Finally, eczema can also have a psychological effect. The appearance of your skin can dramatically affect your self-esteem, which can lead to feelings of depression and anxiety.
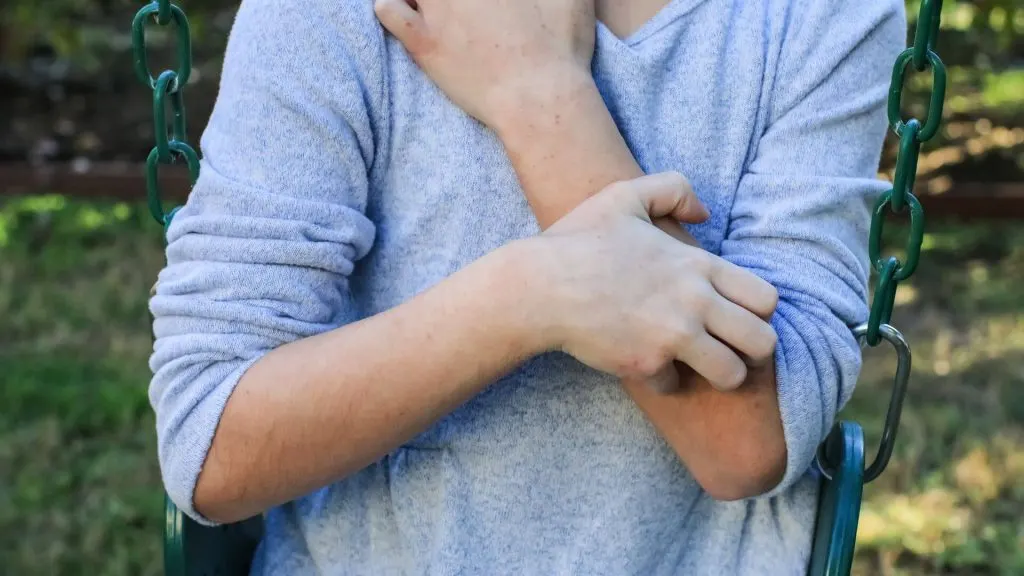

The Diagnostic Process
For those with a history of eczema, it is often easier to diagnose. However, in adults with no history of eczema, it is important that the diagnostic process isn’t rushed because the symptoms of eczema can indicate other health issues too. This is why an evaluation is needed to rule out other possibilities and ensure that it is definitely eczema. A GP can diagnose you, but in some cases, they may refer you to a dermatologist if your eczema is severe or they are concerned about it.
The process can vary between GPs because there is no test for eczema. They tend to rely on whether you have a family or personal history of eczema. Whether you are under a lot of stress and what products you use on your skin. You may then be asked to take an allergy test to see whether you have any skin sensitivities or allergies which could be causing irritation to your skin, a step often recommended by a skin specialist Singapore.
Treatment Options
In all honesty, the treatment options will vary slightly depending on what form of eczema you are diagnosed with, and you can learn more about the different forms of eczema from the Patient. Once you have a diagnosis, your GP can discuss your options with you. Most of the time, this will mean topical treatments and moisturizers, but this can change slightly. For example, if your eczema is triggered by stress, then you might also want to consider a few stress management techniques which can help you to minimize the risk of flare-ups.
As well as topical treatments, you need to think more deeply about the other products that you put on your skin. Any cosmetic or hygiene product that comes into contact with your skin can affect it. Fragrances or chemical irritants can lead to flare-ups. Moisturising is also a huge part of dealing with your eczema. Dry skin is more prone to cracks and other open sores. A doctor might prescribe you a moisturizer or have some recommendations for you. Topical treatments vary in potency, with the strongest being classed as steroids.
Topical steroids are incredibly effective at clearing up eczema flare-ups or infections; however, new research is coming out which suggests that reliance can form between the user and the steroids, which leads to something called topical steroid withdrawal. In addition to topical steroids, there are also oral medications that might be recommended for you, such as oral steroids. Immunosuppressants because eczema can be linked to autoimmune disorders. Finally, there are also biologics, although their use in treating eczema is rare.
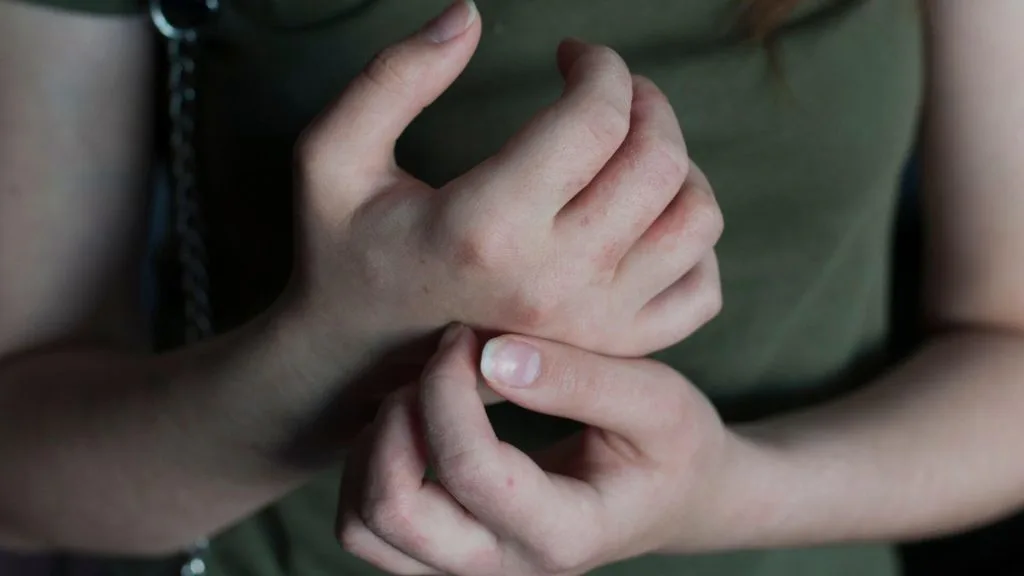

Eczema is classified as a chronic condition; in some instances, it might clear up or go away by itself, but there is no cure for it. That being said, with the right treatment, eczema can be managed. Stress management and moisturising are often the cornerstones for dealing with eczema. Keeping your skin moisturised helps to prevent flare-ups. Allergy tests can also help you to avoid irritants. Finally, remember that your eczema is not your fault; try not to let it affect your self-esteem.
Jessi is the creative mind behind The Coffee Mom, a popular blog that combines parenting advice, travel tips, and a love for all things Disney. As a trusted Disney influencer and passionate storyteller, Jessi’s authentic insights and relatable content resonate with readers worldwide.
